Introduction
In the ever-evolving field of dermatology, biologics have emerged as a groundbreaking and transformative treatment option for a range of skin conditions. These specialized medications harness the power of the body’s own immune system to combat diseases that were once challenging to manage effectively. In this blog, we will explore the use of biologics in dermatology clinics, shedding light on their mechanisms, benefits, and the conditions they are commonly used to treat.
What Are Biologics?
Biologics are a class of medications derived from living organisms, typically proteins, that target specific molecules involved in the immune response. Unlike traditional pharmaceutical drugs, which are synthesized chemically, biologics are created through biotechnological processes. This enables them to precisely target and modulate immune responses, making them a valuable asset in the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory skin diseases.
The Mechanism of Action
Biologics function by selectively inhibiting or stimulating key components of the immune system. In dermatology, they are mainly used to combat chronic inflammatory conditions such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis (eczema), hidradenitis suppurativa, and alopecia areata. Here’s how they work:
- Inhibition of Inflammatory Pathways: Biologics can block inflammatory molecules such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-17 (IL-17), or interleukin-23 (IL-23). By doing so, they reduce the inflammatory response responsible for skin diseases.
- Promotion of Tolerance: Some biologics stimulate regulatory T cells or inhibit specific immune cells, promoting tolerance and reducing the autoimmune response. This is particularly relevant in the treatment of conditions like vitiligo.
Benefits of Biologics in Dermatology
- High Efficacy: Biologics have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in treating a variety of dermatological conditions. Many patients experience significant symptom improvement and disease control.
- Targeted Treatment: Unlike traditional systemic medications, biologics specifically target the molecules responsible for disease progression. This targeted approach minimizes side effects and reduces the risk of systemic toxicity.
- Improved Quality of Life: Patients often report a significant improvement in their quality of life, as biologics can lead to clear skin and relief from pain, itching, and discomfort associated with skin diseases.
- Long-lasting Results: Biologics can provide long-term disease control, and in some cases, induce remission. This can reduce the need for frequent treatments and hospital visits.
Conditions Treated with Biologics
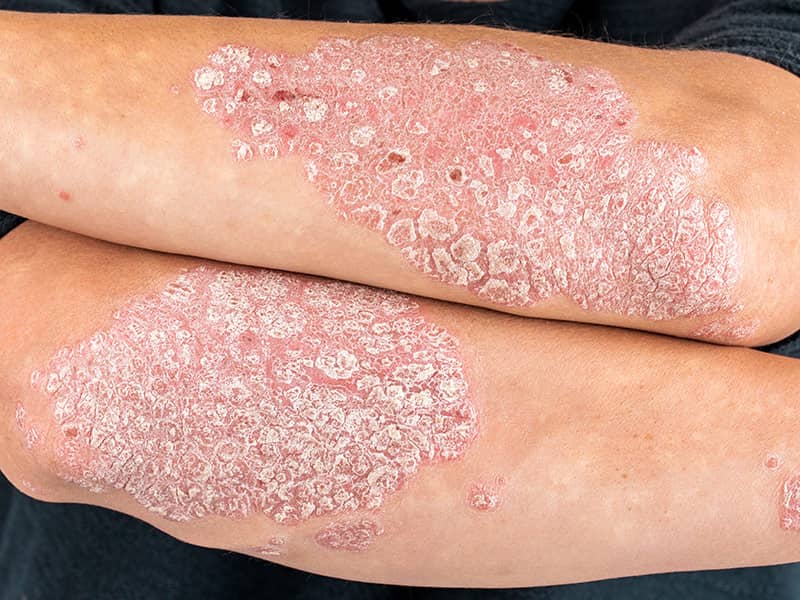
- Psoriasis: Biologics are highly effective in treating moderate to severe psoriasis, offering rapid and sustained symptom relief.
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Some biologics have shown promise in managing atopic dermatitis, particularly in cases resistant to other treatments.
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Biologics can reduce inflammation and the formation of painful nodules in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Alopecia Areata: In some instances, biologics have stimulated hair regrowth in patients with alopecia areata.
- Vitiligo: Biologics are being investigated as potential treatments for vitiligo, with promising results in clinical trials.
Conclusion
Biologics represent a groundbreaking advancement in the field of dermatology, offering targeted and effective treatment options for patients with various skin conditions. While they have revolutionized the management of autoimmune and inflammatory dermatological disorders, it’s essential to note that these medications may not be suitable for all patients. The decision to use biologics should be made in consultation with a dermatologist or healthcare provider, taking into account the specific diagnosis, severity of the condition, and individual patient factors.
As research continues to expand our understanding of biologics and their applications in dermatology, we can anticipate even more innovative treatment options and improved outcomes for patients struggling with skin diseases. The future of dermatology is undeniably intertwined with the promise of biologics, offering hope and relief to countless individuals worldwide.